

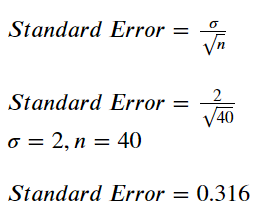
To plot a single standard error as plus/minus ranges (mean ☑ SE), subtract the standard error from the mean for the lower bound. Therefore, the relationship between the standard error of the mean and the standard deviation is such that, for a given sample size, the standard error of the. This provides the standard deviation (SD).ĭivide the standard deviation by the square root of the sample size (n). Sum the squared deviations and divide the total by n-1 (one less than the total number of measurements). Remove negatives by squaring each deviation from the mean. One exception is in regression analysis, where standard error can refer to both the square root of the reduced chi-squared statistic and the standard error for a regression coefficient, such as confidence intervals.Ĭalculate the mean (total of all samples divided by the number of samples) and each measurement's deviation from the mean. In the vast majority of cases, standard error is defined as the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size. The formula for standard deviation is the square root of the sum of squared. By accepting you will be accessing content from YouTube, a service provided by an external third party. Standard deviation is a measure of dispersion of data values from the mean.

Standard error is the measurement of how dispersed a sample’s means are from the population mean. The bootstrap is a nonparametric technique for estimating standard errors and approximate confidence intervals. Please accept YouTube cookies to play this video.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
